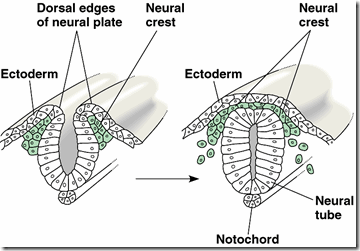
 Neural crest cells are present in the early embryonic period. The neural crest cells are the primitive cells and they, later on, develop into more specialized structures. Following are the derivatives of neural crest cells.
Neural crest cells are present in the early embryonic period. The neural crest cells are the primitive cells and they, later on, develop into more specialized structures. Following are the derivatives of neural crest cells. 1. Connective tissue and bones of the face and skullIf you are practising for a medical examination, for example, USMLE, or PLAB, then you should memorize these because you will get an MCQ about this.
2. Cranial nerve ganglia
3. Cells of the thyroid gland
4. Conotruncal septum in the heart
5. Odontoblasts
6. Dermis in the face and neck
7. Spinal ganglia ( also known as dorsal root ganglia)
8. Sympathetic chain and preaortic ganglia
9. Parasympathetic ganglia of the gastrointestinal tract
10. Adrenal medulla
11. Schwann cells
12. Glial cells
13. Meninges of the forebrain
14. Melanocytes
15. Smooth muscle cells to the blood vessels of the face and forebrain.
Comments
Post a Comment
Post Your Reply and Give Your Opinion About the Post