Author: Kashif Rauf
Mechanical Ventilation
When the patient continues to deteriorate or fails to improve with other measures and oxygen therapy, he needs some respiratory support with mechanical ventilation. Mechanical ventilation improves C02 elimination (confirmed by performing ABG Test) and removes work of breathing, gives relief from exhaustion by giving rest to the respiratory muscles.
1. Non- invasive mechanical ventilation
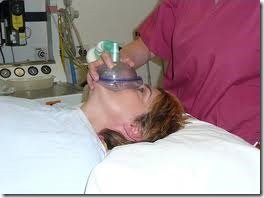
In non- invasive respiration is supported with a face mask or nasal mask so that, endotracheal intubation is avoided. The patient should be conscious, cooperative, be able to breathe spontaneously and cough effectively. This technique is commonly used in acute exacerbation of COPD and pneumonia.
2. Invasive mechanical ventilation
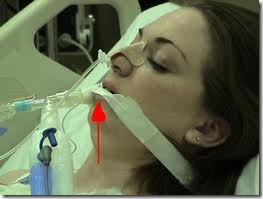
In invasive mechanical ventilation endotracheal tube is passed. The patient may require full or partial support. In full Support, all respiration is controlled by a ventilator that does not allow spontaneous breaths. The patient is deeply sedated with short-acting IV anaesthetic agent and paralyzed with a muscle relaxant. In partial support ventilator helps and augment the patient’s own breaths; it does not require deep sedation and paralysis.
Mechanical Ventilation
When the patient continues to deteriorate or fails to improve with other measures and oxygen therapy, he needs some respiratory support with mechanical ventilation. Mechanical ventilation improves C02 elimination (confirmed by performing ABG Test) and removes work of breathing, gives relief from exhaustion by giving rest to the respiratory muscles.
Types of Mechanical Ventilation:
Mechanical ventilation may be non-invasive or invasive.1. Non- invasive mechanical ventilation

In non- invasive respiration is supported with a face mask or nasal mask so that, endotracheal intubation is avoided. The patient should be conscious, cooperative, be able to breathe spontaneously and cough effectively. This technique is commonly used in acute exacerbation of COPD and pneumonia.
2. Invasive mechanical ventilation

In invasive mechanical ventilation endotracheal tube is passed. The patient may require full or partial support. In full Support, all respiration is controlled by a ventilator that does not allow spontaneous breaths. The patient is deeply sedated with short-acting IV anaesthetic agent and paralyzed with a muscle relaxant. In partial support ventilator helps and augment the patient’s own breaths; it does not require deep sedation and paralysis.
Indications of Mechanical Ventilation
Indications of mechanical ventilation are listed below- Respiratory failure not responding to medical treatment.
- Head injury - controlled hyperventilation to reduce intracranial pressure.
- Chest injury.
- Severe pulmonary oedema
Weaning from Respiratory Support:
This is the process of progressively reducing and eventually removing all external ventilatory support and associated apparatus. If the apparatus is suddenly removed, the patient may be unable to breathe because of respiratory muscle weakness and residual decreased lung compliance.Complications of Mechanical Ventilation:
- Tube in one lung causes a collapse of the other lung.
- Fall in cardiac output due to positive pressure in lung and thorax that reduces venous return.
- Ventilator-induced lung injury such as barotraumas due to over-distension of alveoli leading to pneumomediastinum, subcutaneous emphysema and pneumothorax.
- Nosocomial (hospital acquired) pneumonia.
- Abdominal distension and ileus.
Modes of Mechanical Ventilation
NON-INVASIVE RESPIRATORY SUPPORT
| Used in acute exacerbation of COPD, pulmonary oedema and the postoperative collapse of the lung. May be used with endotracheal intubation or tightly fitting face mask |
| |
| Used in acute exacerbation of COPD |
| INVASIVE RESPIRATORY SUPPORT | |
| Appropriate for initial control of patient with little respiratory drive |
| IT allows the patient to breathe spontaneously between the mandatory tidal volumes delivered by the ventilator. |
| Spontaneous breaths are augmented by a preset level of positive pressure (positive pressure means above atmospheric pressure) |
| The pressure is given throughout the expiration. Helps in re-expand collapse or edematous lung. |
Comments
Post a Comment
Post Your Reply and Give Your Opinion About the Post