Definition of Anemia/What is Anemia:
 Anaemia may be defined as a state in which the blood haemoglobin level is below 13.5 g/dl in an adult male and below 11.5 g/dl in an adult female.
Anaemia may be defined as a state in which the blood haemoglobin level is below 13.5 g/dl in an adult male and below 11.5 g/dl in an adult female.Symptoms Of Anemia:
Those problems which can be described a patient are called symptoms. For example, a patient can tell a doctor that he has a fever, headache, back pain, abdominal pain etc, All these are symptoms.Symptoms of Anemia are given below:
- Fatigue
- A headache
- Faintness
- Breathlessness
- Angina of effort
- Palpitation
- Intermittent claudication
Signs Of Anemia:
Signs are elicited by a doctor or another person, the patient may be unaware of them, for example, a patient may tell you that he has a fever, but he may not tell you that he has yellow or pale eyes or tachycardia (rapid heart beats). So, yellow or pale eyes and tachycardia are signs.Signs of Anemia are given below:
Non-specific Signs of Anemia:
Following signs can be present in anemia of all types
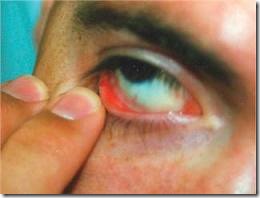
- Paler skin, conjunctiva & mucous membrane
- Tachycardia
- High volume pulse
- Ankle oedema
- Heart failure
- Systolic flow murmur
Specific Signs of Anemia:
Following signs are present in specific types of anaemia (not in all types), So these are specific signs of anaemia.

- Koilonychia (spoon-shaped nails) - in iron deficiency.
- Jaundice - in hemolytic anaemia
- Bone deformities - in thalassemia major
- Leg ulcers - in sickle cell anaemia
Comments
Post a Comment
Post Your Reply and Give Your Opinion About the Post