Type 2 ( Antibody Mediated ) Hypersensitivity Reaction-Mechanism-Diseases and Examples
•Type 2 hypersensitivity reaction is mediated by antibodies directed against the Antigens (intrinsic or extrinsic and normal or altered) present on the cell surface or extracellular matrix.
MECHANISM OF TYPE II (ANTIBODY MEDIATED) HYPERSENSITIVITY
There are three mechanisms of type two hypersensitivity reactions. Each Mechanism gives rise to different clinical manifestation.
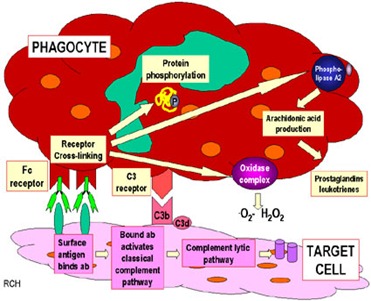
•1)- Opsonization of cells by antibodies and complement components and ingestion by phagocytes.
In this mechanism, antibodies are formed against antigens present on the cell surface. Antibodies opsonize the antigens for phagocytosis. Moreover, these Antibodies also stimulate the complement system which further opsonizes the cells for phagocytosis). Opsonization is a process in which antibodies combine with antigens and which are then recognized by the phagocytes for phagocytosis.
•2)- Inflammation induced by antibodies binding to Fc receptors of leukocytes and by complement breakdown products.
In this mechanism, The Antibodies attach to the cell surface Antigens through fab component while at the same time to Fc receptors of leukocytes through the Fc component. The leukocytes are thus stimulated and release injurious substances like enzymes and reactive O2 species resulting in damage to tissues. The antibodies also stimulate the complement factors producing C5a (chemotactic factor) attracting more leukocytes towards the site of injury/damage.
•3)- Anti- receptor Abs disturb the function of the receptors:
In this mechanism, Antibodies are formed against the cell surface receptors (which are considered as antigens) specific for some other hormone, neurotransmitter etc and impair their function either by stimulating them or blocking them.
Examples Of Type two Hypersensitivity Reactions and Diseases;
Diseases of mechanism 1:
Transfusion reactions, Erythroblastosis fetalis, Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia, Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
Diseases of mechanism 2:
Good pasture Syndrome (Nephritis and Lung haemorrhage), Rejection of transplant, Rheumatic Fever
Diseases of mechanism 3:
Myasthenia Gravis, Graves Disease, Pernicious Anemia, insulin resistant D.M, Pemphigus Vulgaris.

Comments
Post a Comment
Post Your Reply and Give Your Opinion About the Post