 |
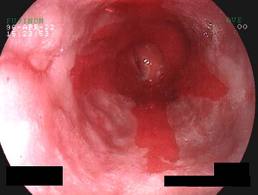
| Barrett's oesophagus. red velvety appearance |
Barrett's Esophagus (Oesophagus)
Definition and causes:
It is an oesophagal disorder caused by prolonged gastro-oesophagal reflux disease, characterized by replacement of normal squamous epithelium by columnar epithelium at the lower end of the
oesophagus.
Morphology:
Macroscopic and Microscopic study will reveal the following features.
1. Oesophagal mucosa appear red velvety
2. Metastatic columnar epithelium of the stomach is present at the lower end of the oesophagus.
3. Sometime Metastatic columnar Columnar epithelium contains intestinal goblet cells.
4. Low-grade or high-grade dysplasia may be present which may lead to adenocarcinoma.
Complications:
1. Ulceration
2. Bleeding
3. Stricture
4. Development of adenocarcinoma
Treatment:
Following treatment options may be considered;
1. Proton pump inhibitors to control GERD ( gastroesophageal reflux disease)
2. Esophagectomy: that is the removal of the oesophagus
3. Endoscopic resection of the oesophagal mucosa.
Because There is a high risk of oesophagal cancer in individuals with Barrett's oesophagus therefore extensive treatment is done.