It is a tumour of the adrenal medulla ( or sympathetic ganglia ) that secretes excess catecholamines ( that is epinephrine and norepinephrine)
Adrenal gland has two main layers, cortex and medulla, the cortex is further subdivided into 3 zones and every zone secretes a specific set of hormones.
The adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine. In normal conditions, adrenal medulla secretes catecholamines after the stimulation of the sympathetic nervous system. Hence sympathetic overactivity or adrenal medulla tumour will result in increased secretion of catecholamines. These excessive catecholamines result in symptoms of pheochromocytoma.
Symptoms:
1. CNS: Headache, dizziness, anxiety
2. CVS (cardiovascular): Tachycardia, Palpitations, Hypertension,
3. Respiration: Increased rate and depth of respiration
4. GIT ( Gastrointestinal tract): Nausea and vomiting.
5. Skin: Pale, cool, moist, increase sweating.
Diagnosis:
There is increase urinary secretion of, catecholamines, conjugates of catecholamines and VMA that is vanillyl mandelic acid. The high concentration of this chemical will strongly suggest Pheochromocytoma. Moreover, CT scan and ultrasonography or MRI show an abnormally enlarged adrenal gland at the superior pole of the kidney.
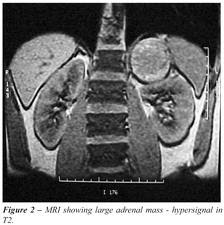 |
| MRI showing a large adrenal mass on the left side. |
Treatment.
Surgical Removal of a tumour.

Comments
Post a Comment
Post Your Reply and Give Your Opinion About the Post